Product Usage: This product is designated as a "Novelty Peptide" and is intended solely for specialized applications in controlled settings. It is not intended for any specific biological, therapeutic, or diagnostic use. All information provided on this website is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be construed as guidance for any particular application or usage.
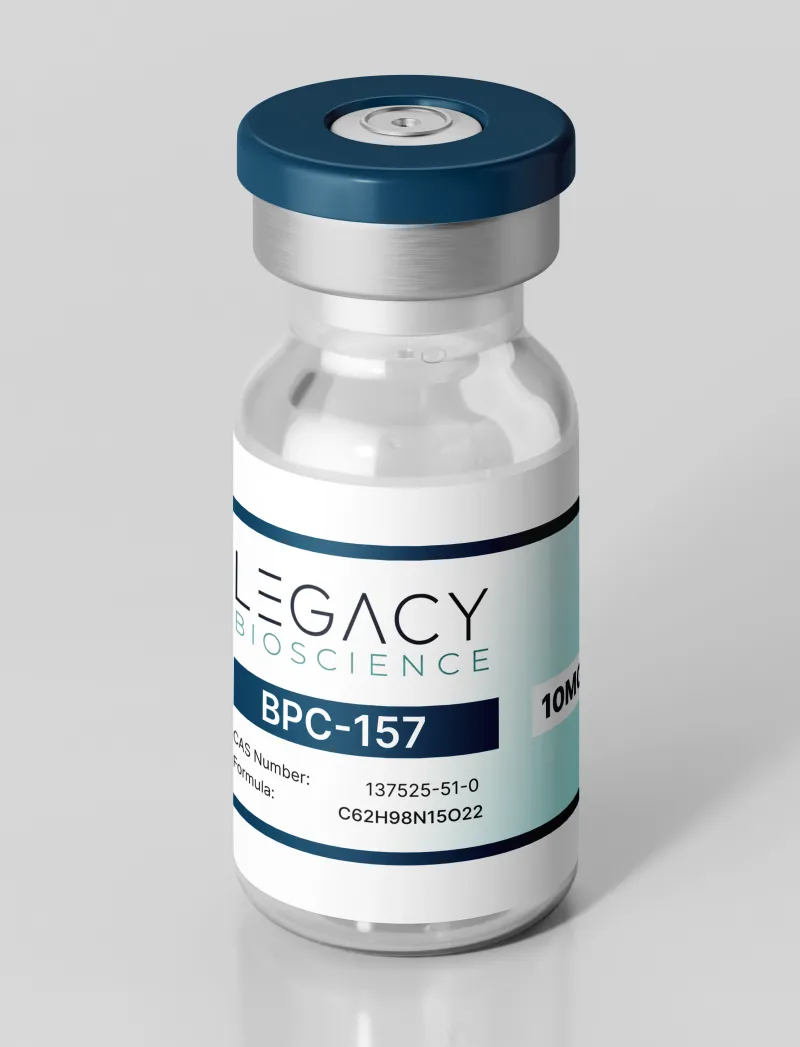
What Is BPC-157 10MG?
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound 157) is a synthetic pentadecapeptide derived from a protective protein found in human gastric juice. This 15-amino acid peptide has gained significant attention in research for its potential therapeutic effects across various physiological systems. BPC-157 has demonstrated remarkable healing properties, particularly in gastrointestinal and musculoskeletal tissues, as well as neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects.
Structure

Sequence:Gly-Glu-Pro-Pro-Pro-Gly-Lys-Pro-Ala-Asp-Asp-Ala-Gly-Leu-Val
Molecular Formula:C62H98N16O22
Molecular Weight:1419 Da
CAS Number:137525-51-0
Research Findings
- Gastrointestinal Healing: BPC-157 has shown significant gastroprotective effects, promoting healing of gastric ulcers and potentially benefiting inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) by reducing inflammation and improving symptoms in animal models.
- Musculoskeletal Repair: Studies have demonstrated BPC-157's ability to accelerate tendon, ligament, and muscle healing. It has been particularly effective in promoting tendon outgrowth, cell survival, and cell migration in tendon healing processes.
- Neuroprotection: BPC-157 has exhibited neuroprotective properties, potentially benefiting conditions such as traumatic brain injury and stroke. It has been shown to counteract injuries due to hippocampal ischemia/reperfusion in rat models.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: The peptide has demonstrated potent anti-inflammatory properties across various tissues, contributing to its healing and protective effects.
- Angiogenesis Promotion: BPC-157 has been observed to promote angiogenesis, which may contribute to its healing effects in various tissues.
Future Research Directions
- Human Clinical Trials: While BPC-157 has shown promising results in animal studies, more extensive human clinical trials are needed to establish its efficacy and safety in various conditions.
- Mechanism of Action: Further research is required to fully elucidate the molecular mechanisms by which BPC-157 exerts its diverse effects.
- Long-term Effects: Studies investigating the long-term effects and potential side effects of BPC-157 administration are necessary.
- Delivery Methods: Research into optimal delivery methods and dosing regimens for different conditions could enhance the therapeutic potential of BPC-157.
- Combination Therapies: Exploring the potential synergistic effects of BPC-157 with other therapeutic agents could open new avenues for treatment.
References
- Sikiric, P., et al. (2018). Novel cytoprotective mediator, stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Vascular recruitment and gastrointestinal tract healing. Curr. Pharm. Des., 24, 1990-2001. [Online].
Available: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29879878/ - Gwyer, D., et al. (2019). Gastric pentadecapeptide body protection compound BPC 157 and its role in accelerating musculoskeletal soft tissue healing. Cell Tissue Res., 377, 153-159. [Online].
Available: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30982100/ - Vukojevic, J., et al. (2020). Rat inferior caval vein (ICV) ligature and particular new insights with the stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Vascul. Pharmacol., 106, 54-66. [Online].
Available: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31698062/ - Sikiric, P., et al. (2013). The influence of a novel pentadecapeptide, BPC 157, on N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methylester and L-arginine effects on stomach mucosa integrity and blood pressure. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 332, 23-33. [Online].
Available: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9298922/ - Chang, C.H., et al. (2011). The promoting effect of pentadecapeptide BPC 157 on tendon healing involves tendon outgrowth, cell survival, and cell migration. J. Appl. Physiol., 110, 774-780. [Online].
Available: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21030672/ - Seiwerth, S., et al. (2014). BPC 157's effect on healing. J. Physiol. Paris, 91, 173-178. [Online].
Available: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9403788/